Raspberry Pi based Digital Measurement System in Physics
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
|
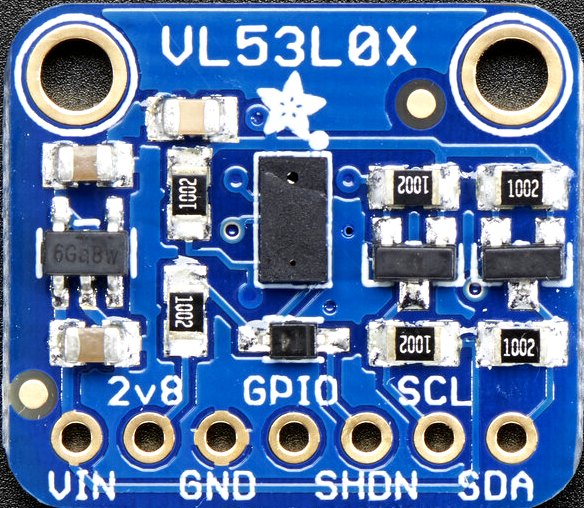
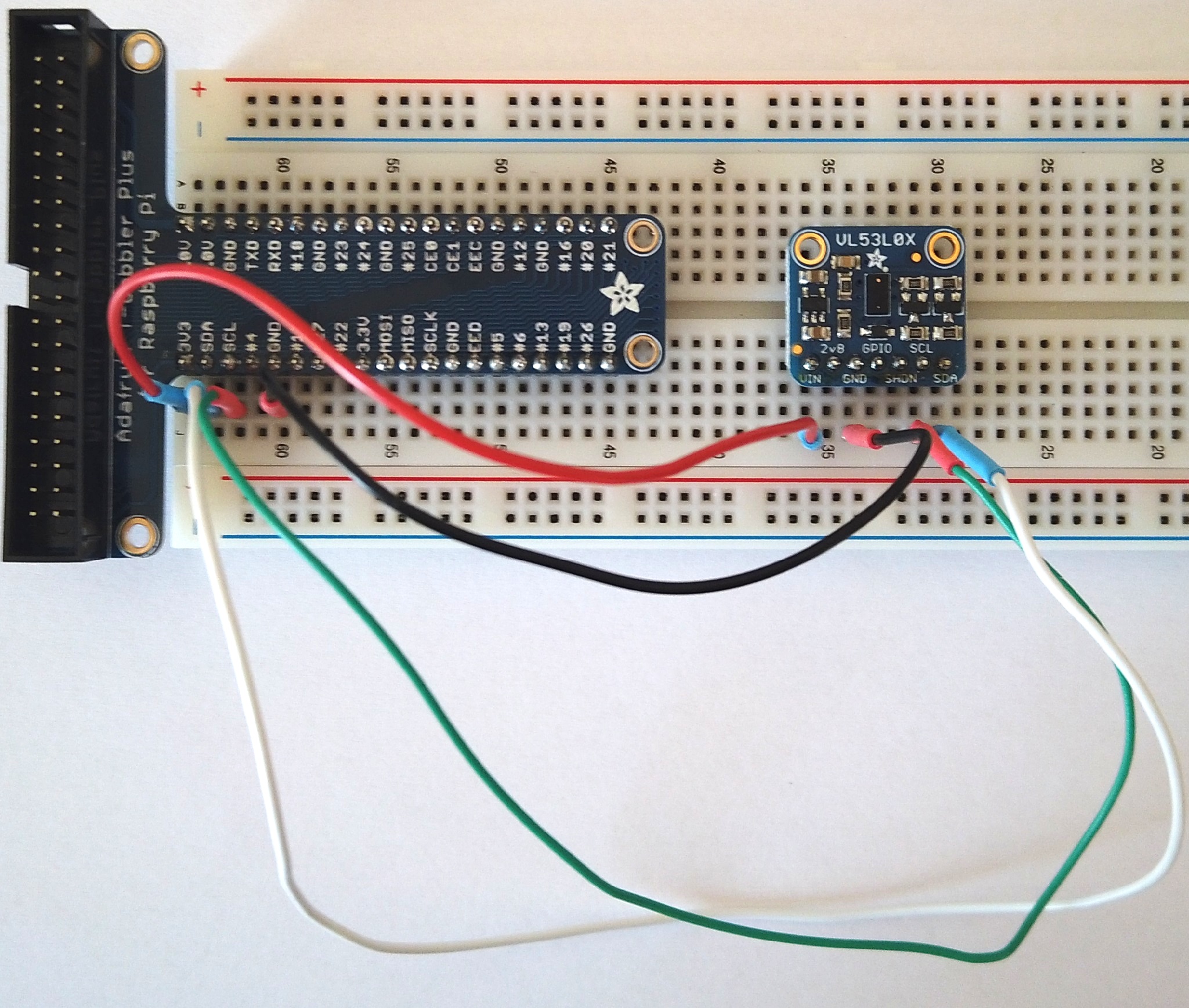
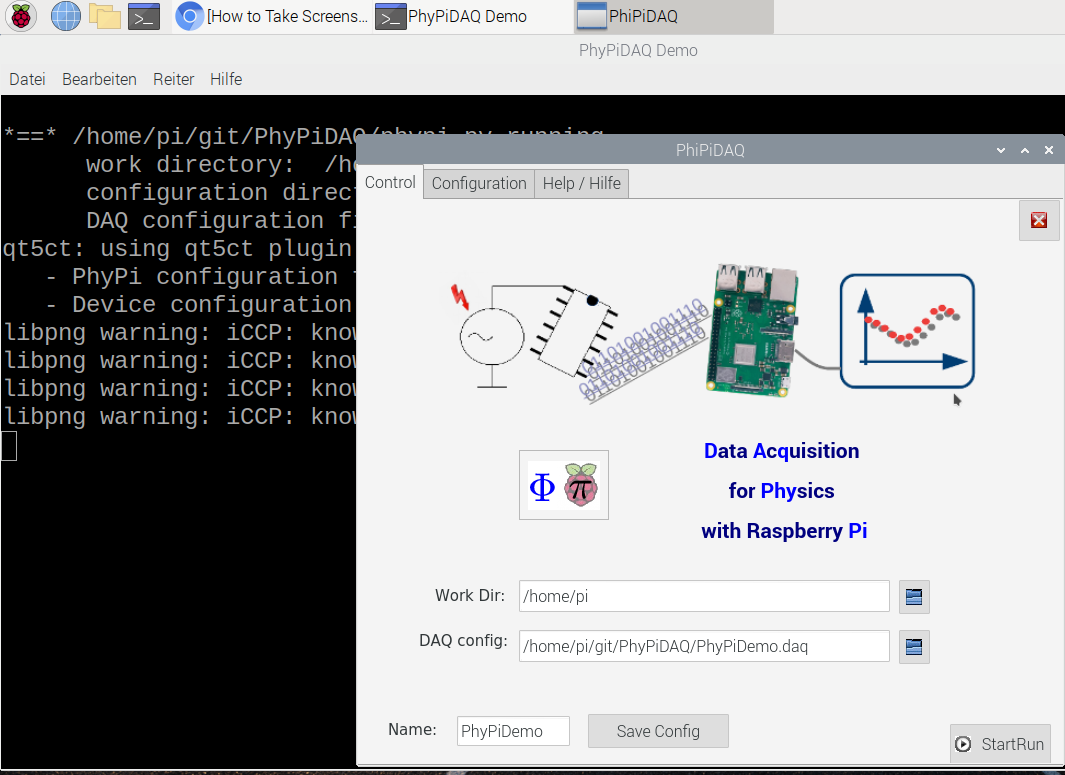
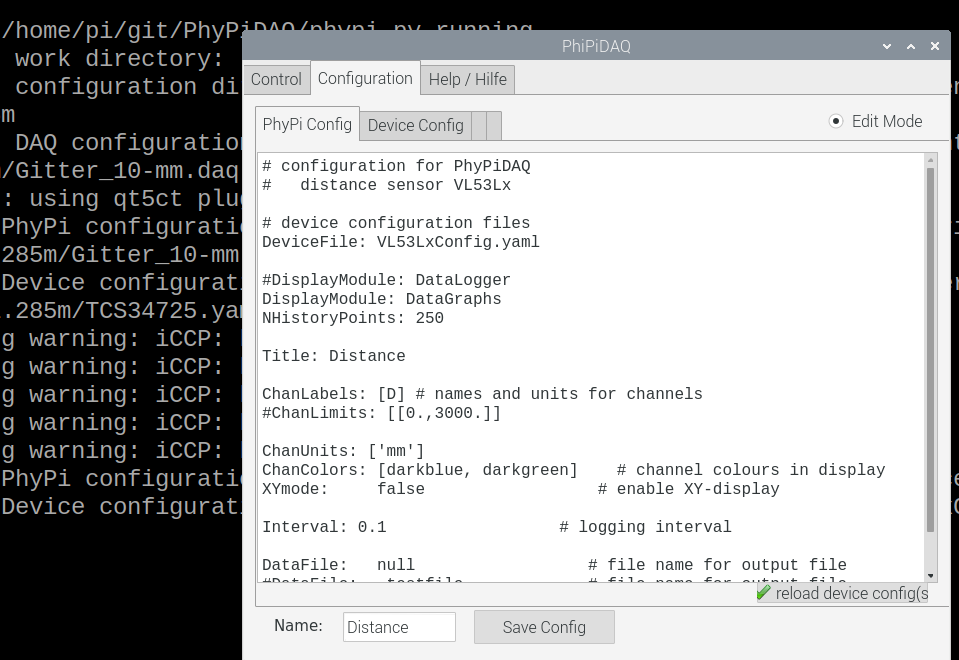
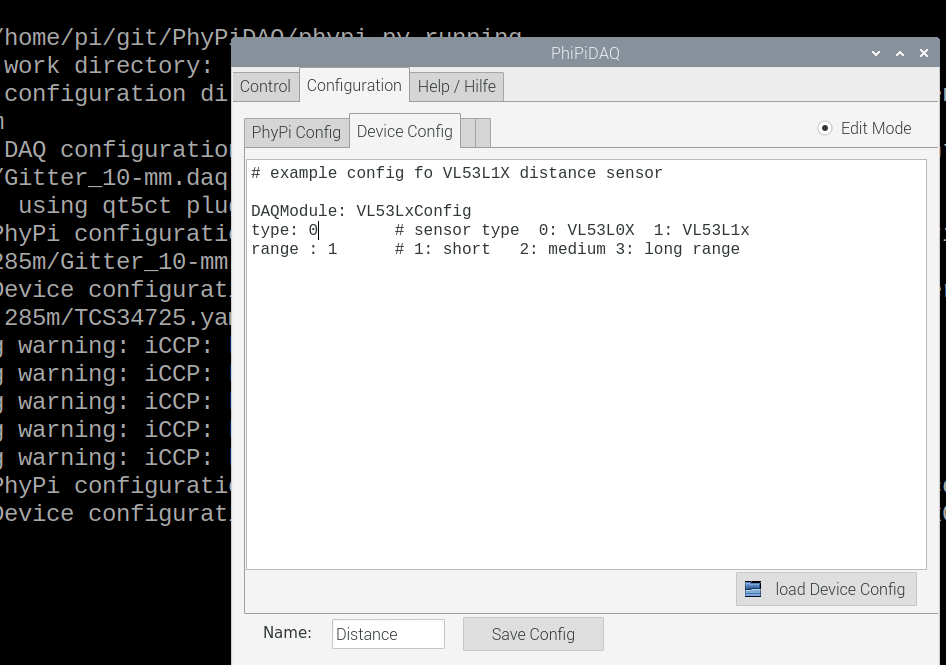
Connecting the VL53L0X laser-ranging module to the PhyPiDAQ measuring system, one can record and visualise the position of an object in real-time. The measured data can be saved in .csv files for further analysis. Some experiments are listed below.
|